The Visconti-Sforza Tarot, c.1460
This pack of tarot cards appears to have have been made in the Bembo workshop in Cremona for Bianca Maria Visconti, c.1460.
The tarot deck - carte de trionfi - was invented in northern Italy in the first half of the fifteenth century. This luxury hand-painted example was probably made for the courtly milieu of Francesco Sforza who married the only child of Filippo Maria Visconti in 1441. It is an extended four-suit pack, including pages, knights, queens and kings, plus 22 trionfi, making a total of 78 cards. Many cards contain either heraldic motifs, aristocratic, militaristic attire or inscriptions such as “a bon droyt” or “amor myo”. Currently this venerable set is divided between the Accademia Carrara in Bergamo (26 cards), the private Colleoni collection also in Bergamo (13 cards), and the Pierpont Morgan Library in New York (35 cards). Four cards have been lost. Where the pack was previously attributed to Antonio Cicognara new research has instead atttributed the deck to the workshop of Bonifacio Bembo (active c.1442-1477), which specialised in early-Renaissance paintings, murals, altarpieces and other decorated objects.

Above: cards from the facsimile edition of "I Tarocchi dei Visconti" published by Dal Negro, Treviso, Italy. This almost complete 15th Century Tarot deck is believed to have been produced in the Bonifacio Bembo workshop in the early 1460s. Cards are made from pasteboard with opaque paint on tooled gold ground. The original deck has 74 of the assumed original 78 cards, the missing cards are The Devil, The Tower, Three of Swords and Knight of Coins.
Some possible correspondences, even a close relationship, between early Italian and early German cards, can be noted. For example a similarity between the knave of coins in this deck with the unter (lower knave) of stags in the pack engraved by the Master of the Playing Cards which recurs in the woodcut Maihingen sheet►
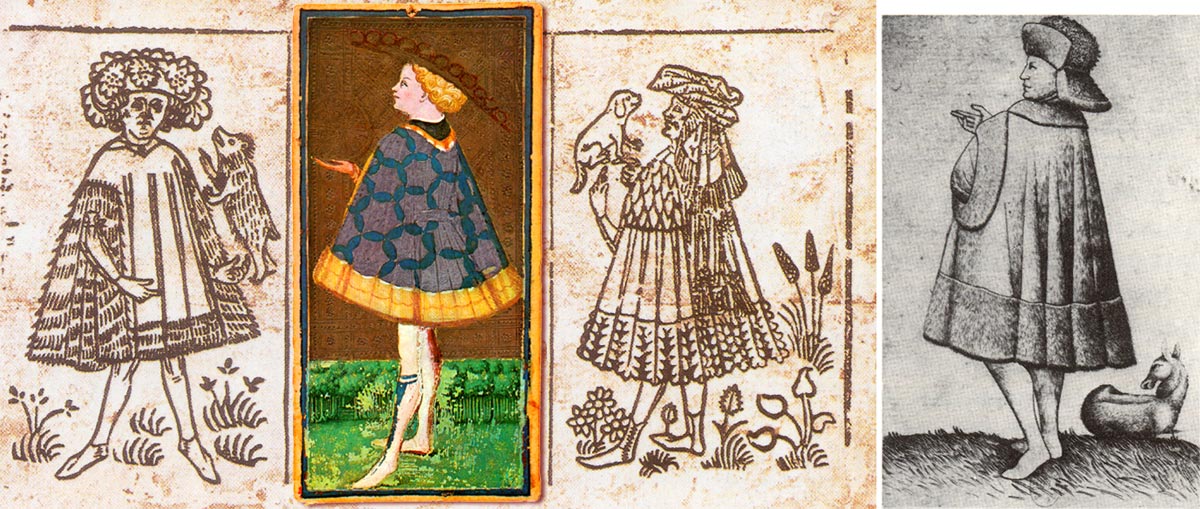

Above: correspondences between early Italian and early German cards.
The 22 ‘Trionfi’ Cards
The 22 ‘trionfi’ cards (‘trumps’ or ‘arcana’), which are added to the regular pack to make up a complete tarot deck, served as trump cards which beat any normal cards in a trick. These 22 extra cards contain images which are both decorative and moralising and may have been intended raise the intellectual level of the game.
Were these 22 ‘trionfi’ a complete set of existing pictorial images taken from somewhere else, or a newly created set for this particular game?
Games requiring special sets of picture cards are recorded in the inventory of the engraver Francesco Rosselli in 1523, named «giuocho del trionfo del petrarcha» [game of triumphs of Petrarch]; «giuco d’apostoli chol nostro singnore» [game of the apostles of our lord)]; «giuoco di sete virtù»; [game of the seven virtues] etc. Earlier, the so-called «Tarocchi di Mantegna» of c.1465 is a set of 50 allegorical engravings depicting a humanist world view.
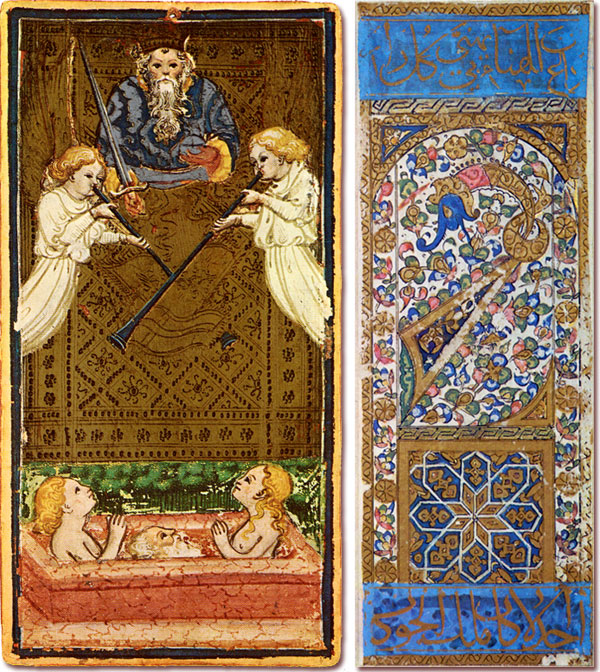

Above: the Visconti-Sforza Judgement card and a hand-drawn and painted Mamluk playing card, XV or early XVI century.
This also brings to mind the Islamic Mamluk cards which contain rhyming aphorisms on the court cards which are often very enchanting and uplifting: “As for the present that rejoices, thy heart will soon open up“ - “I will, as pearls on a string, be lifted in the hands of kings” - “May God give thee prosperity; then thou will already have achieved thy aim” - “Rejoice for thy lasting happiness” - “I am as a flower, a string of pearls is my soil?” - “The alif rejoices and fulfils your wishes” - “Whosoever will call me to his happiness, he will only see joyful looks”.
According to Michael Pearce (2015), the figure on Bembo’s first trionfi card corresponds closely to the archetype of the late medieval natural magician – a scholar, writer and sage. See: project AWE►
Copies of the Visconti-Sforza deck
Michael Dummett (2007) has pointed out that the Visconti-Sforza deck was copied, in particular the six cards which he attributes to Benedetto Bembo, younger brother of Bonifacio, by other artists. The pin holes at the top of each card do suggest that they were given or lent as artist’s models to other painters (this possibly explains how four cards are now missing). There are several incomplete sets extant which contain one or more cards copied from this deck, sometimes reversed, sometimes with the original orientation. But other cards do not correspond with these models and contain different imagery (see below comparison of Death card). So, the subjects of the cards had become established, but artistic arrangement or iconographic details were left to the painter or draftsman to vary.
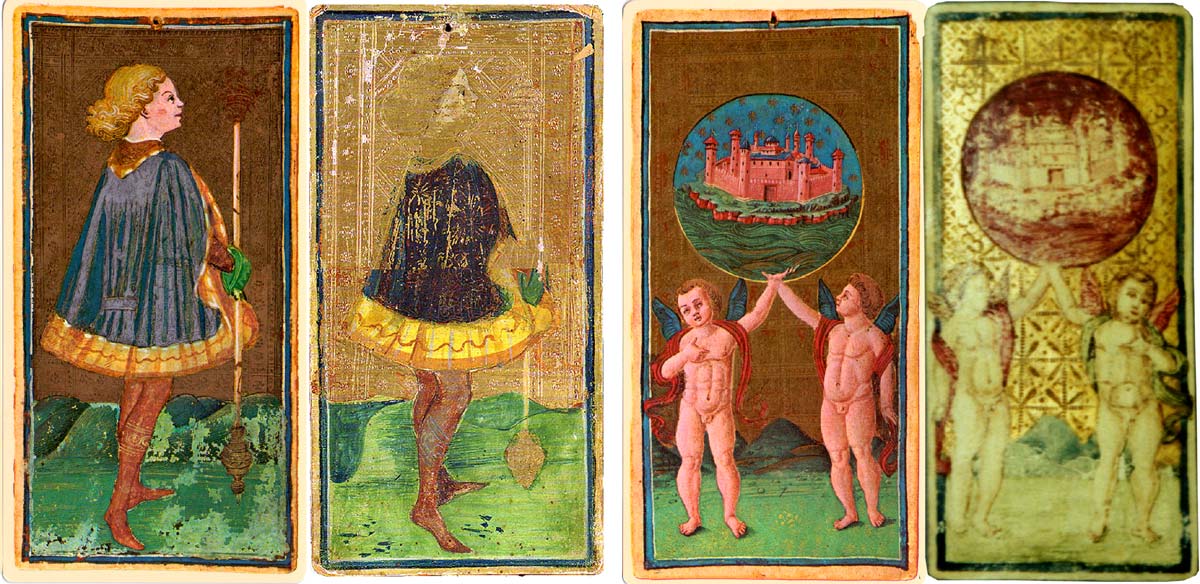
Above: two examples of copied cards. The right-hand card is one of the four Guildhall Library Tarocchi Cards from the Worshipful Company of Makers of Playing Cards collection of historic playing cards (and is the only one without a pin hole). Dummett also mentions the four cards in the Victoria and Albert Museum one of which is copied from the Visconti-Sforza deck. The Victoria and Albert set includes the Death card with Death as a skeleton wearing a cardinal's hat and cape which is different from the Visconti-Sforza Death card.
Comparison of Death card
Although the subjects of the cards had become established, artistic arrangement or iconographic details were left to the painter or draftsman to vary, according to their influences and inspiration.
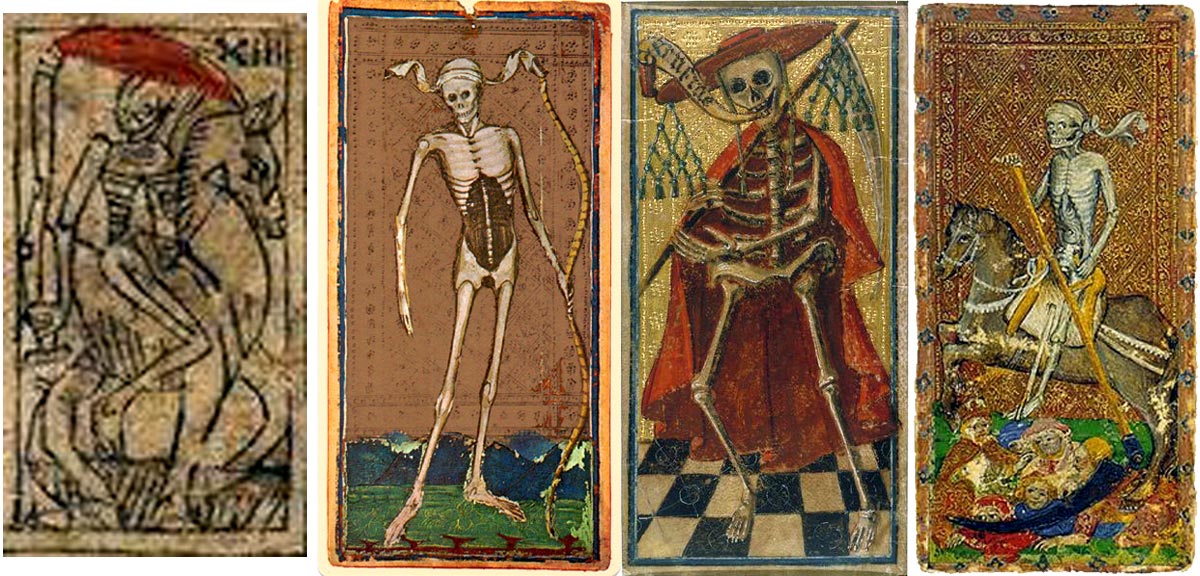

Above: mid-XV century Italian tarot view more►
Above: The Visconti-Sforza Tarot, c.1460
Above: one of the four cards in the Victoria and Albert Museum
Above: the Cary-Yale Visconti deck
In the notes to The Waste Land, T. S. Eliot wrote: “I do not know the exact constitution of the tarot deck.” There is nothing of the kind; there exist distinct forms of the tarot deck, each different in composition.
REFERENCES and ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The Morgan Library & Museum: Visconti-Sforza Tarot Cards►
Dummett, Michael: Six XV-Century Tarot Cards: Who Painted Them?, Artibus et Historiae, Vol. 28, No. 56, 2007, pp. 15-26.
Hoffmann, Detlef: The Playing Card, an illustrated history, Edition Leipzig, 1973
Husband, Timothy B: The World in Play, Luxury Cards 1430-1540, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, 2015
Pratesi, Franco: In Search of Tarot Sources, The Playing-Card vol.27 No.2 (1998) pp.64-68; No.3 (1999) pp.111-116. Online here►
Thanks to Samten de Wet for additional research.

By Simon Wintle
Member since February 01, 1996
I am the founder of The World of Playing Cards (est. 1996), a website dedicated to the history, artistry and cultural significance of playing cards and tarot. Over the years I have researched various areas of the subject, acquired and traded collections and contributed as a committee member of the IPCS and graphics editor of The Playing-Card journal. Having lived in Chile, England, Wales, and now Spain, these experiences have shaped my work and passion for playing cards. Amongst my achievements is producing a limited-edition replica of a 17th-century English pack using woodblocks and stencils—a labour of love. Today, the World of Playing Cards is a global collaborative project, with my son Adam serving as the technical driving force behind its development. His innovative efforts have helped shape the site into the thriving hub it is today. You are warmly invited to become a contributor and share your enthusiasm.
Related Articles

Magyar Tarot
Hungarian fortune-telling cards with surreal and unconventional designs.

Late flowering of the Lyon pattern
Faustino Solesio’s late version of the Lyon pattern from about 1870.

Tarot Beirut
A beautiful Arabic Tarot : a mystical tool for positive guidance and well-being.

Czech National Patterns by S.D. Modiano
Modiano produced cards with the Prague and Trappola patterns in the early 20th century.

Emilio Tadini playing cards
Beautiful dreamlike playing card designs by Emilio Tadini.

Tarot de las Coscojas
Historical playing card design, tarot symbolism and an almost psychedelic medieval surrealism.

Tarot de Valverde de la Vera
A series of 24 surrealist engravings by Mexican artist Claudio Favier in which archetypal Tarot alle...

Austrian Tarock by S.D. Modiano
Modiano’s Austrian Tarock with country scenes has been in production for over 100 years.

Le carte da gioco Arcimboldo
Courts and suit-signs inspired by the works of the Italian Renaissance painter, Giuseppe Arcimboldo....

22 Pittori in 22 Arcani
Collaborative Tarot with contributions from 22 different Italian artists including Menegazzi and Tav...

Tarock Cards by NIL Spielkartenfabrik
A deck of tarock cards from the eastern end of the ending Austro-Hungarian Empire.

Justice playing cards
Ethical concepts in a deck produced by Riccardo Conturbia’s Passione Playing Cards Ltd.

Tarot hiéroglyphique égyptien
The design of the cards draws inspiration from various religious and philosophical traditions merged...

Alan Tarot Deck
Reprint of a Tarock pack originally designed by Argio Orell for the Austrian Lloyd shipping company....

Tarot Baraja Egipcia
Curious Tarot with Egyptian-style trumps issued by Franco Mora Ruiz from Mexico.

Le Tarot de Sète
Reinterpretation of the Tarot de Marseille by Julien Labat, an artist from Sète.
Most Popular
Our top articles from the past 28 days










